Closed-loop approach
Many of the corrugated base paper grades considered in this life cycle database incorporate recovered fibres, and all of the paper grades achieve a high level of recycling after use, and the fibres themselves will be recycled multiple times.
This potentially introduces complexity to the analysis, as choices have to be made regarding the allocation of impacts between the primary fibre-based paper and the recovered fibre based paper, in particular:
• the impacts of the primary fibre pulp production and the final waste treatments
• the avoided impacts resulting from the recycling.
However, for the production of corrugated base papers a closed loop recycling situation is considered – i.e., the recovered material is assumed to be used in the same product life cycle. In this case, the collected fibres displace the input of primary fibres, and the need for allocation is avoided (as per ISO 14044).
Thus, to simplify the system, recycling of corrugated board may be considered as processing of the primary fibre after use in corrugated board or as raw material processing for the secondary product (or recycled products), also used in corrugated board. This is an appropriate and justifiable simplification as the main raw material for the recovered paper mills producing corrugated base papers is used corrugated board, thus flows in and out of the system of other kinds of paper are ignored.
The closed-loop approach requires that the total system is considered during a certain period of time and a specific geographic area. A simplified system for a closed-loop corrugated board packaging system is given in Figure 11.
There are different definitions for recycling and recovery (which could mean collection of waste or treatment of waste), depending on the application. This of course leads to the publication of different recycling/recovery rates.
For example, CEN 13440:2003 describes a procedure for calculating the rate of material recycling to demonstrate compliance with the recycling targets given in the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive 94/62/EC (as amended by 2018/852/EC).
For the system described in Figure 11, fibres are recovered (in the sense of collected) from shavings from the production of corrugated board and from collected corrugated board after use, and following that are recycled in a papermaking process to become new paper.
Figure 11 - Illustrating the closed-loop approach
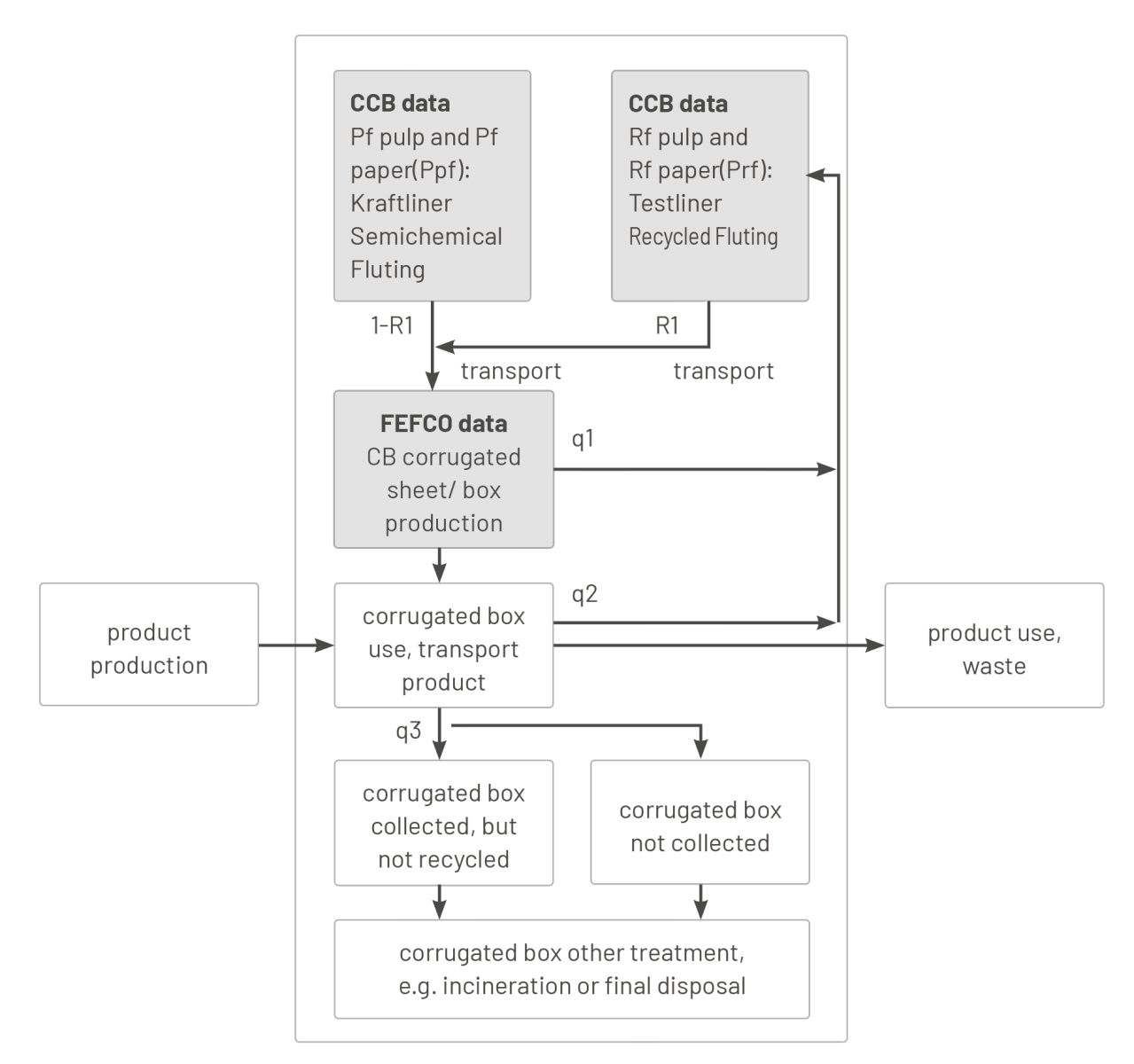
The recycled fibre content (R1) for this report is defined as total recovered fibre recycled from shavings (q1) as well as from used corrugated boxes (q2) divided by the total paper production used for corrugated board production.
- q1 is defined as the weight of production shavings from corrugated board production divided by the weight of the base paper used for the corrugated board production. These production shavings are always recycled. The amount depends on the reference unit. For Europe, the typical amount is about 100 kg/tonne corrugated product, for the converted box it is 120 kg total shavings/tonne.
- q2 is defined as the weight of collected corrugated board after use, effectively recycled divided by the weight of the base paper used for corrugated board production. Recycling is the common practice for collected (and if necessary sorted) corrugated board, but it may be that fibres are lost from the loop because not all corrugated packaging is collected. For corrugated board that is not recycled, other recovery options, such as incineration with energy recovery may take place. According to an estimation based on CEPI statistics for 2014, about 87% (R2) of the corrugated board used in Europe was collected and recycled.
In a simplified system for closed-loop corrugated board packaging, this means that the percentage of recovered material is equal to (R2 x [1- rsh ]) = 87% x [1 – 0.120] = 76.6% of the input of the base papers would be recycled after use if all the recovered corrugated board was recycled only within the system. This is a simplification as a small part of the recovered fibre input originates from, for example, graphic paper loops and some collected corrugated board is recycled into other paper grades7 .
For the purposes of this document, imports and exports of the corrugated board system are ignored, as are used packaging imports and exports. The application of this specific assumption means that the recycling rate of corrugated board (shavings + used packaging) is equal to the recovery rate of these products.
Table 2 shows that the average R1 for Europe in 2022 is about 88%. In this simplified approach this roughly corresponds with the total amount of collected shavings and used packaging as a percentage of the weight of the input of the base papers for the corrugated board production ([q1 + q2]/total paper production =~ 90%), showing the validity of the closed-loop approach.
Note rsh is not included in the calculation of the recycling rate according to the Directive on Packaging and Packaging Waste 94/62/EC and R2 does not include organic recycling as defined for the same purpose. Therefore, the recycling rate differs from the rate calculated to assess compliance with the recycling targets according to the Directive.
7 Based in the equation presented in Figure 11, the life cycle of the paper fibres in corrugated packaging is estimated to be fully circular at 87%. Within the context of the European recovered paper production environment, recovered fibres will typically be sent for use at the nearest appropriate recycled paper manufacturer. This may not necessarily be a packaging paper line. Some 60% of packaging is recovered at mills producing recycled paper for packaging, some 12% originate from other paper types such as recovered newsprint and the rest, 12% is clippings and trimmings from corrugating and conversion manufacturing.
Definitions and calculations of recovery and recycling
Definitions of recovery and recycling EN 13193
Definitions set for the Directive on packaging and packaging waste 94/96/EC, as amended by Directive 2018/852/EC.
Recycling: any recovery operation by which waste materials are reprocessed into products, materials or substances whether for the original or other purposes. It includes the reprocessing of organic material but does not include energy recovery and the reprocessing into materials that are to be used as fuels or for backfilling operations.
Material recovery: any recovery operation, other than energy recovery and the reprocessing into materials that are to be used as fuels or other means to generate energy. It includes, inter alia, preparing for re-use, recycling and backfilling.
Packaging waste: any packaging or packaging material covered by the definition of waste laid down in Article 3 of Directive 2008/98/EC, excluding production residues.
Calculation of recycling rate EN 13440: 2003
rη = (δ1 + δ2)/(α+ß-γ)
rη = recycling rate of used packaging
δ1 = material for organic recycling
δ2 = material for material recycling
α = quantity of packaging put on the market for one way use
ß = quantity of reusable packaging put on the market and used for the first time
γ = that part of used packaging which is not available for recycling due to other secondary uses
CEPI Recycling rate calculation
Recycling rate = utilisation of paper for recycling + net trade of paper for recycling, compared to paper & board consumption.
In 2017, the European Paper recycling rate (for all grades and products) was 72.3% (CEPI key statistics 2017) in Europe (EU-27 countries + Norway and Switzerland), meaning that over 55 million tons of paper-based products have been collected for recycling.
Concerning the Paper & Board Packaging recycling rate in Europe, according to CEPI statistics 2017, it amounts to 82.1%.

