Boundaries and declared unit
The gate-to-gate life cycle inventories for each grade of corrugated base papers are presented in the Annex according to the following declared unit:
one air dry tonne (1000 kg) of net saleable paper at the parent reel, before conversion to finished products
The gate-to-gate inventory for conversion of corrugated base papers into corrugated board and boxes is presented in the Annex according to the following declared unit:
one tonne (1000 kg) of printed, slotted, folded and glued corrugated boxes
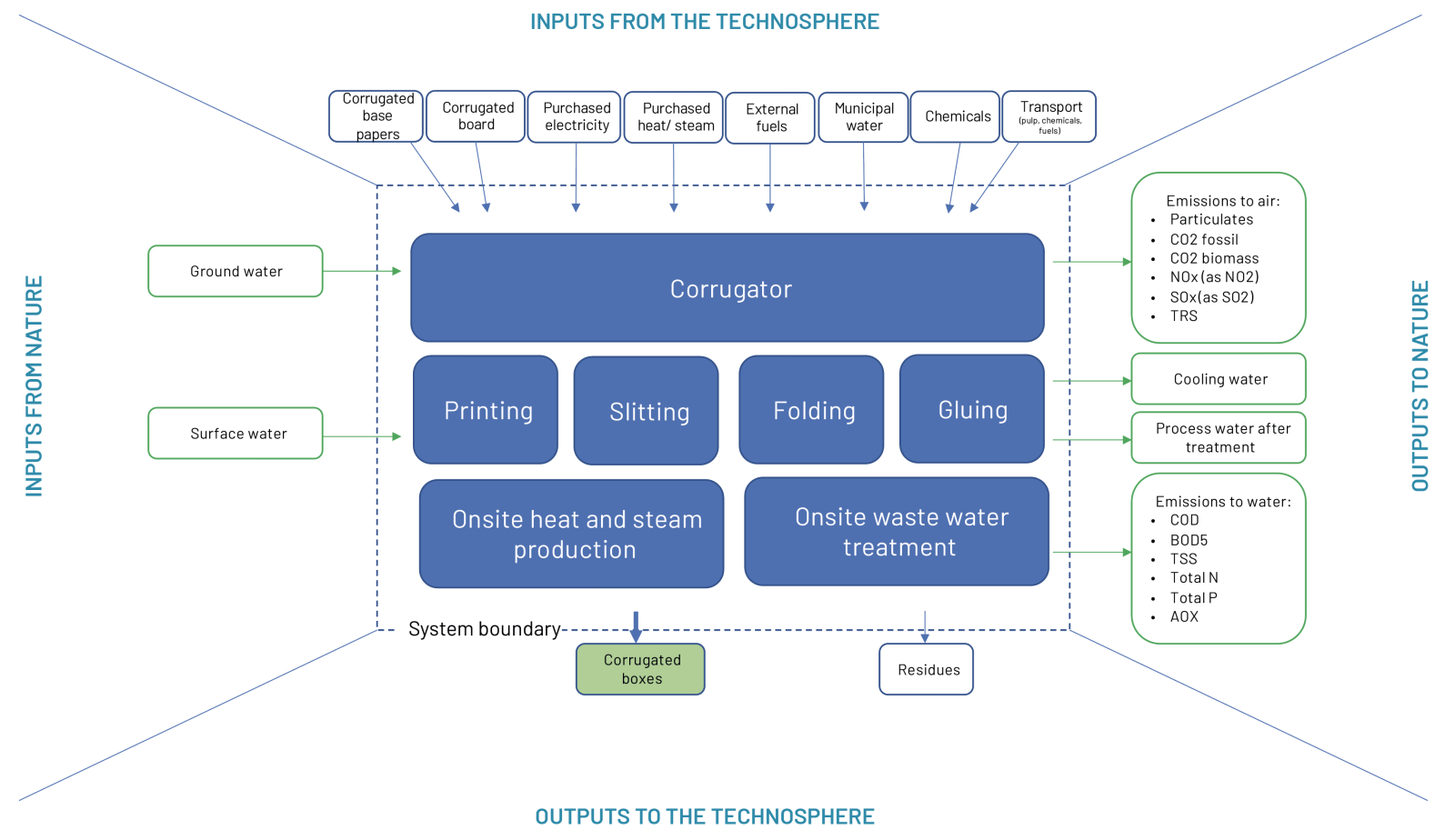
The compiled results presented in Table 4 of this report relate to the production one tonne (1000kg) of printed, slotted, folded and glued corrugated boxes. The system boundaries considered for these results consider and quantify the flows to and from the technosphere and the environment from the papermill in-gate to corrugated box plant out-gate, as illustrated in Figure 8. In order to complete a cradle-to-gate analysis for corrugated boxes, life cycle data for the items shown in red must be added.
Figure 8 - System boundaries for the results shown in Table 3
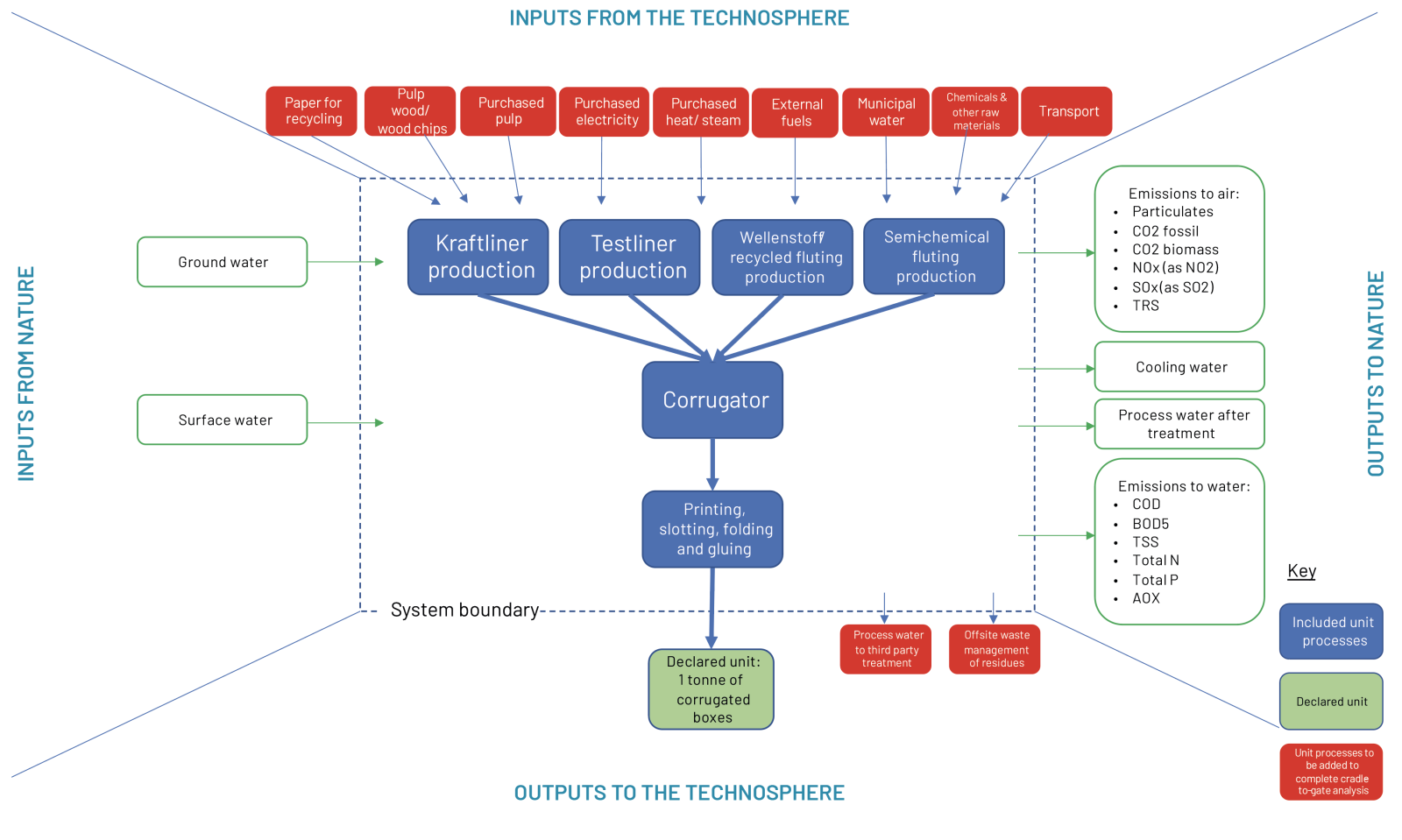
In addition to the compiled results shown in Table 4, separate data is presented in the Annex for production of the corrugated base paper grades (kraftliner, testliner recycled fluting and semi chemical fluting) and for the conversion of corrugated base papers into corrugated boxes (corrugating plus printing, slotting, folding and gluing). The system boundaries for these separate datasets are described below.
System boundaries for corrugated base papers
The system boundaries of the life cycle inventories for corrugated base papers presented in the Annex include all activities within the pulp and papermill boundaries. Thus, included in the inventory are all the inputs and outputs (from/to the technosphere and from/to nature) associated with:
•Pulp production from pulp wood/wood chips
•Pulp production from paper for recycling
•Stock preparation, refining, and operation of the paper machine
•Drying
•Reeling and reel winding
•Supporting activities used in paper production, e.g. water and solid waste treatment, onsite electricity and heat/steam generation.
Figure 9 summarises the system boundaries. These system boundaries are representative of the core processes.
Figure 9: Gate-togate system boundaries - production of corrugated base paper
In cases where the mill produces and sells excess energy (e.g. electricity or steam), this is treated as a multifunctional situation. The system provides two functions (i.e. corrugated base paper plus energy). In this case, subdivision has been applied – i.e. only the inputs and outputs that are allocated to the paper production are reported in the life cycle inventory.
No allocation was made to by-products such as tall oil, turpentine and wood/bark chips, so the reported inputs and outputs include the production of these by-products.
For those paper mills producing more than one grade of paper and/or market pulp it is necessary to allocate inputs and outputs to the different paper grades or pulp. Mill staff who filled in the questionnaire have made the allocation according to causality.
Data has been collected relating to the following key non-fibre inputs to the pulp and papermaking processes:
•Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
•Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
•Oxygen (O2)
•Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
•Sodium Chlorate (NaClO3)
•Calcium oxide (CaO)
•Chlorine dioxide (ClO2)
•Sodium bisulphite (NaHSO3)
•Ground calcium carbonate (GCC)
•Precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) – purchased
•Clay
•Wet strength agent
•Dry strength agent
•Synthetic binders (latex)
•Starch – maize
•Starch – potato
•Starch – corn/wheat
•Starch - cationic
The total mass of other non-fibre inputs not listed above is below 1% of the paper weight. As a general
rule, these other non-fibre inputs could have been omitted from the study as insignificant. However, for completeness all non-fibre inputs for which data was reported by more than 6 mills have been included in the inventory.
System boundaries for corrugated board and boxes
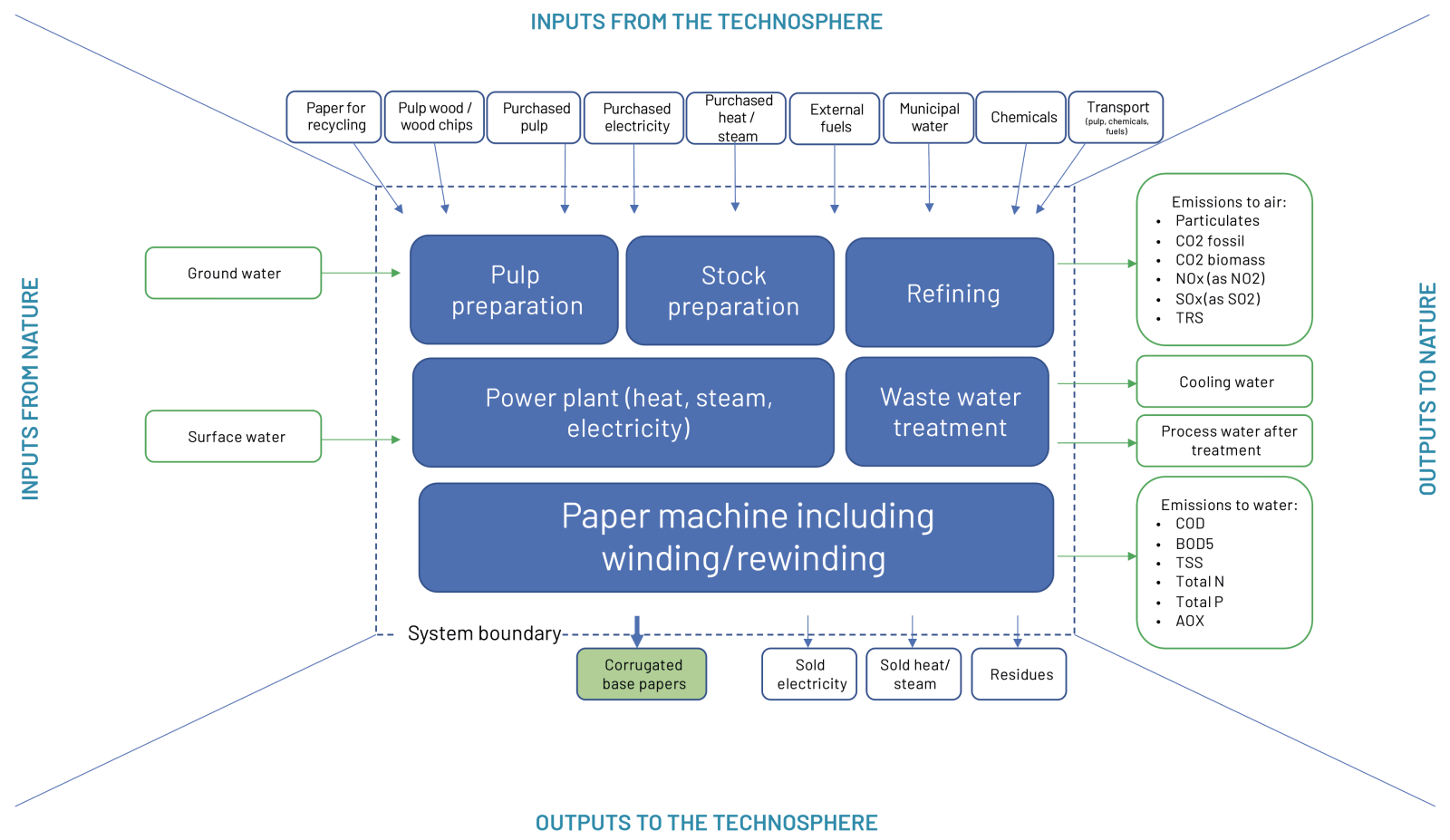
The system boundaries of the life cycle inventory for conversion of corrugated base papers into corrugated board and boxes presented in the Annex include all activities associated with assembling corrugated base papers into corrugated board and converting corrugated board into corrugated boxes. Thus, included in the inventory are all the inputs and outputs (from/to the technosphere and from/to nature) associated with:
• The corrugator machine
• Printing
• Slotting
• Folding
• Gluing
• Supporting activities used in conversion process, e.g. onsite heat/steam generation, onsite wastewater treatment.
Figure 10 summarises the system boundaries.
Figure 10 - Gate-to-gate system boundaries – production of corrugated board and corrugated boxes